What’s the point?
Widgets are classes used to build UIs.
Widgets are used for both layout and UI elements.
Compose simple widgets to build complex widgets.
The core of Flutter’s layout mechanism is widgets. In Flutter,almost everything is a widget-even layout models are widgets.The images,icons,and text that you see in a Flutter app are all widgets.But things you don’t see are also widgets,such as the rows,columns,and grids that arrange,constrain,and align the visible widgets.
You create a layout by composing widgets to build more complex widgets. For example,the first screenshot below show 3 icons with a label under each one.

The second screenshot displays the visual layout,showing a row of 3 columns where each column contains an icon and a label.
Note:Most of the screenshots in this tutorial are display with debugPaintSizeEnabled set to true so you can see the visual layout.For more information,see Visual debugging ,a section in Debugging Flutter apps.
Here’s s diagram of the widget tree for this UI:
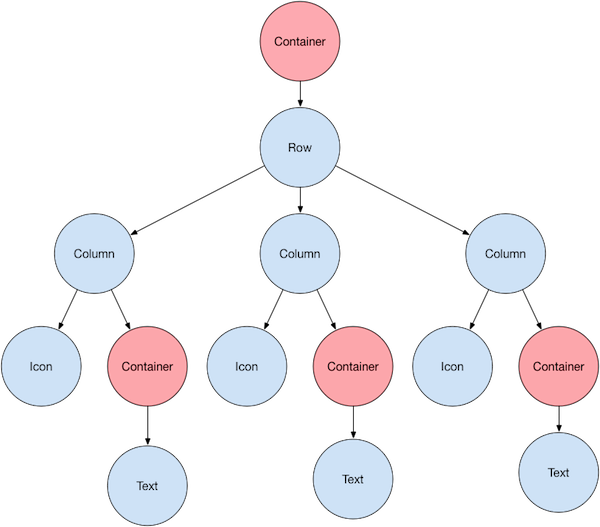
Most of this should look as you might expect,but you might be wondering about the containers(shown in pink).Container is a widget class that allows you to customize its child widget.Use a Container when you want to add padding,margins,borders, or background colors,to name some of its capabilities.
In this example,each Text widget is placed in a Container to add margins. The entire Row is also placed in a Container to add padding around the row.
The rest of the UI in this example is controlled by properties. Set an Icon‘s color using its color property. Use the Text.style property to set the color,weight,and so on. Columns and Rows have properties that allow you to specify how their children are align vertically or horizontally,and how much space the children should occupy.
The code is follow:
import 'package:flutter/material.dart';
class FirstLayoutPage extends StatelessWidget {
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return Scaffold(
appBar: AppBar(
title: Text('First Layout'),
),
body: Center(
child: Container(
padding: const EdgeInsets.all(4.0),
height: 100,
child: Row(
mainAxisAlignment: MainAxisAlignment.spaceEvenly,
children: <Widget>[
Column(
mainAxisAlignment: MainAxisAlignment.center,
children: <Widget>[
Icon(
Icons.call,
color: Colors.blue,
size: 35,
),
Container(
margin: EdgeInsets.only(top: 10),
child: Text(
'CALL',
style: TextStyle(
fontSize: 18,
color: Colors.blue,
fontWeight: FontWeight.bold),
),
)
],
),
Column(
mainAxisAlignment: MainAxisAlignment.center,
children: <Widget>[
Icon(
Icons.navigation,
color: Colors.blue,
size: 35,
),
Container(
margin: EdgeInsets.only(top: 10),
child: Text(
'ROUTE',
style: TextStyle(
fontSize: 18,
color: Colors.blue,
fontWeight: FontWeight.bold),
),
)
],
),
Column(
mainAxisAlignment: MainAxisAlignment.center,
children: <Widget>[
Icon(
Icons.share,
color: Colors.blue,
size: 35,
),
Container(
margin: EdgeInsets.only(top: 10),
child: Text(
'SHARE',
style: TextStyle(
fontSize: 18,
color: Colors.blue,
fontWeight: FontWeight.bold),
),
)
],
)
],
),
),
),
);
}
}Lay out a widget
How do you layout a single widget in Flutter? This section shows you how to create and display a simple widget. It also shows the entire code for a simple Hello World app.
In Flutter,it takes only a few steps to put text,an icon,or an image on the screen.
- Select a layout widget
Choose from a variety of layout widgets based on how you want to align or constrain the visible widget,as these characteristics are typically passed on to the contained widget.
The example uses Center which centers its content horizontally and vertically.
- Create a visible widget
For example,create a Text widget.
Text('Hello World'),Create an Image widget.
Image.asset(
'images/lake.jpg',
fit: BoxFit.cover,
),Create an Icon widget.
Icon(
Icons.star,
color: Colors.red[500],
),- Add the visible widget to the layout widgetee
All layout widgets have either of the following:
A child property if they take a single child - for example,Center or Container
A children property if they take a list of widgets - for example,Row,Column,ListView,or Stack.
Add the Text widget to the Center widget:
Center(
child: Text('Hello World'),
),- Add the layout widget to the page
A Flutter app is itself a widget,and most widgets have a build() method. Instantiating and returning a widget in the app’s build() method displays the widget.
Material apps
For a Material app, you can use a Scaffold widget,it provides a default banner,background color,and has API for adding drawers,snack bars,and bottom sheets. Then you can add the Center widget directly to the body property for the home page.
class MyApp extends StatelessWidget{
Widget build(BuildContext context){
return MaterialApp(
title: 'Flutter layout demo',
home: Scaffold(
appBar: AppBar(
title: Text('Flutter layout demo'),
),
body: Center(
child: Text('Hello World'),
),
),
);
}
}Note: The Material library implements widgets that follow Material Design principles. When designing your UI, you can exclusively use widgets from the standard widgets library, or you can use widgets from the Material library. You can mix widgets from both libraries,you can customize existing widgets, or you can build your own set of custom widgets.
Non-Material apps
For a non-Material app,you can add the Center widget to the app’s build() method:
class MyApp extends StatelessWidget{
Widget build(BuildContext context){
return Container(
decoration: BoxDecoration(color: Colors.white),
child: Center(
child: Text(
'Hello World',
textDirection: TextDirection.ltr,
style: TextStyle(
fontSize: 32,
color: Colors.black87,
),
),
),
);
}
}Note: The above code is in the main.dart and invoke the main() method directly!
A layout widget should add to a page.
void main => runApp(MyApp());Lay out multiple widgets vertically and horizontally
One of the most common layout patterns is to arrange widgets vertically or horizontally. You can use a Row widget to arrange widgets horizontally, and a Column widget to arrange widgets vertically.
What’s the point?
Row and Column are two of the most commonly used layout patterns.
Row and Column each take a list of child widgets.
A child widget can itself be a Row,Column,or other complex widget.
You can specify how a Row or Column aligns its children,both vertically and horizontally.
You can stretch or constrain specific child widgets.
You can specify how child widgets use the Row’s or Column’s available space.
To create a row or column in Flutter,you add a list of children widgets to a Row or Column widget. In turn,each child can itself be a row or column,and so on. The following example shows how it is possible to nest rows or columns inside of rows or columns.
This layout is organized as a Row. The row contains two children:a column on the left,and an image on the right:
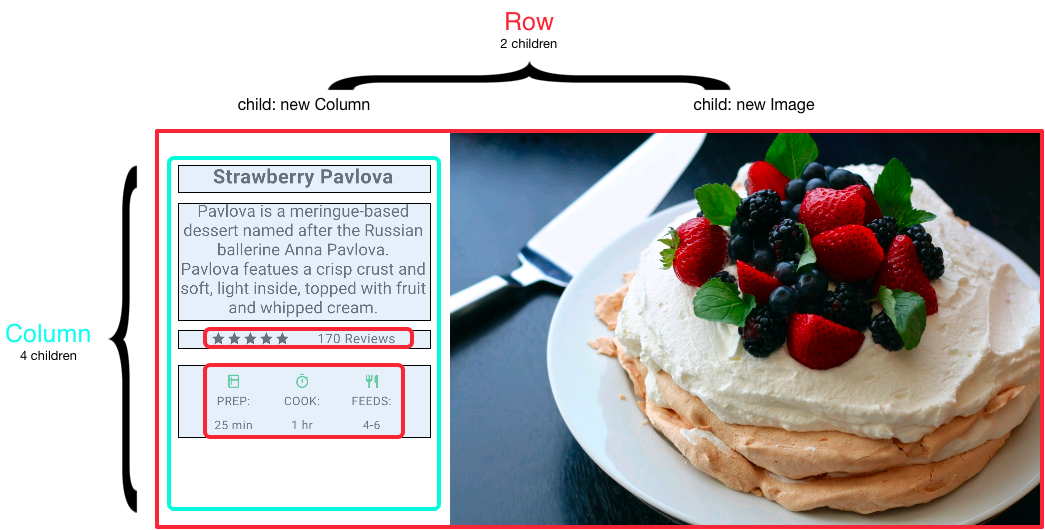
The left column’s widget tree nests rows and columns.
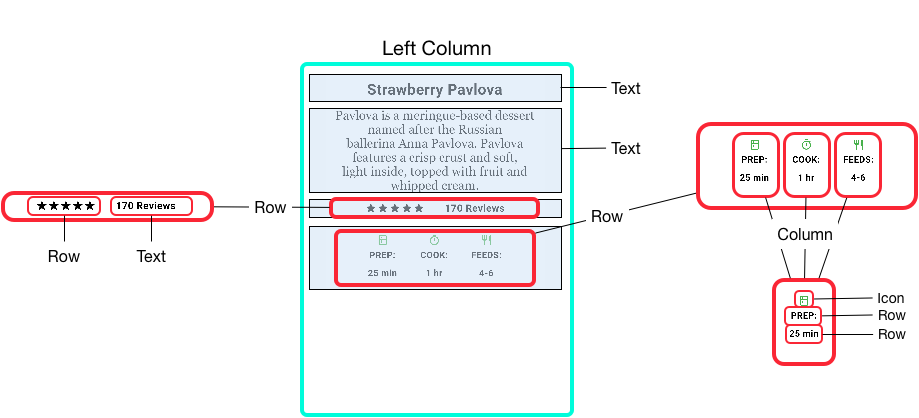
Nesting rows and columns
The layout framework allows you to nest rows and columns inside of rows and columns as deeply as you need. Let’s look the code for the outlined section of the following layout:
The outlined section is implemented as two rows. The ratings row contains five stars and the number of reviews. The icons row contains three columns of icons and text.
The widgget tree for the ratings row:
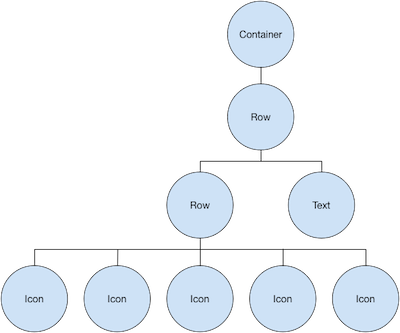
The ratings variable creates a row containing a smaller row of 5 star icons,and text:
var stars = Row(
mainAxisSize: MainAxisSize.min,
children: <Widget>[
Icon(Icons.star, color: Colors.green[500]),
Icon(Icons.star, color: Colors.green[500]),
Icon(Icons.star, color: Colors.green[500]),
Icon(Icons.star, color: Colors.black),
Icon(Icons.star, color: Colors.black),
],
);
final ratings = Container(
padding: const EdgeInsets.all(20),
child: Row(
mainAxisAlignment: MainAxisAlignment.spaceEvenly,
children: <Widget>[
stars,
Text('170 Reviews',
style: TextStyle(
color: Colors.black,
fontWeight: FontWeight.w800,
fontFamily: 'Roboto',
letterSpacing: 0.5,
fontSize: 20,
))
],
),
);Tip: To minimize the visual confusion that can result from heavily nested layout code,implement pieces of the UI in variables and functions!
The icons row,below the ratings row,contains 3 columns;each column contains an icon and two lines of text,as you can see in its widget tree:
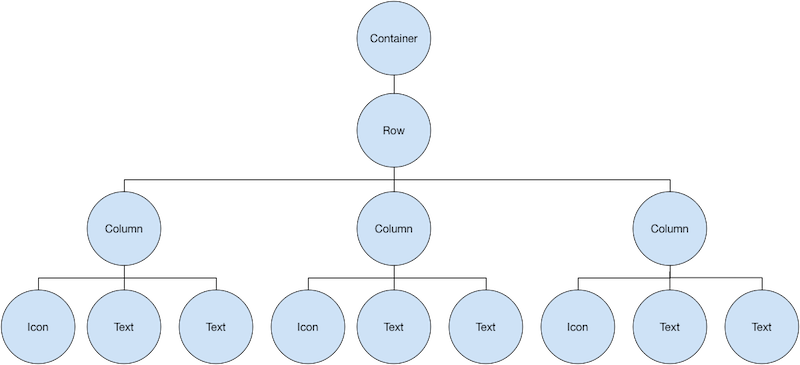
The iconList variable defines the icons row:
final descTextStyle = TextStyle(
color: Colors.black,
fontWeight: FontWeight.w800,
fontFamily: 'Roboto',
letterSpacing: 0.5,
fontSize: 18,
height: 2,
);
//DefaultTextStyle.merge() allows you to create a default text
//style that is inherited by its child and all subsequent children.
final iconList = DefaultTextStyle.merge(
style: descTextStyle,
child: Container(
padding: const EdgeInsets.all(20),
child: Row(
mainAxisAlignment: MainAxisAlignment.spaceEvenly,
children: <Widget>[
Column(
children: <Widget>[
Icon(
Icons.kitchen,
color: Colors.green[500],
),
Text('PREP:'),
Text('25 min'),
],
),
Column(
children: <Widget>[
Icon(
Icons.timer,
color: Colors.green[500],
),
Text('COOK:'),
Text('1 hr'),
],
),
Column(
children: <Widget>[
Icon(
Icons.restaurant,
color: Colors.green[500],
),
Text('FEEDS:'),
Text('4-6'),
],
)
],
),
));The leftColumn variable contains the ratings and icons rows,as well as the title and text that describes the Pavlova:
final titleText = Container(
padding: const EdgeInsets.all(20),
child: Text('Strawberry Pavlova',
style: TextStyle(
fontWeight: FontWeight.w800,
letterSpacing: 0.5,
fontSize: 30,
)),
);
final subTitle = Text(
'Pavlova is a meringue-based dessert named after the Russian ballerina'
'Anna Pavlova. Pavlova features a crisp crust and soft,light inside,'
'topped with fruit and whipped cream.',
textAlign: TextAlign.center,
style: TextStyle(
fontFamily: 'Georgia',
fontSize: 25,
));
final leftColumn = Container(
padding: EdgeInsets.fromLTRB(20, 30, 20, 20),
child: Column(
children: <Widget>[
titleText,
subTitle,
ratings,
iconList,
],
),
);The left column is placed in a Container to constrain its width. Finally,the UI is constructed with the entire row (containing the left column and the image)inside a Card.
The Pavlova image is from Pixabay. You can embed an image from the net using Image.network() but,for this example,the image is saved to an images directory in the project,added to the pubspec file,and accessed using Image.asset(). For more information,see Add assets and images.
body: Center(
child: Container(
margin: const EdgeInsets.fromLTRB(0, 40, 0, 30),
height: 600,
child: Card(
child: Row(
crossAxisAlignment: CrossAxisAlignment.start,
children: <Widget>[
Container(
width: 440,
child: leftColumn,
),
mainImage,
],
),
),
),
),Tip: The Pavlova example runs best horizontally on a wide device,such as a tablet. If you are runing this example in the IOS simulator,you can select a different device using the Hardware > Device meun. For this example,we recommend the iPad Pro. You can its orientation to landscape mode using Hardware > Rotate. You can also change the size of the simulator window (without changing the number of logical pixels) using Window > Scale.
The final code is:
import 'package:flutter/material.dart';
class NestingRowsAndColumnsPage extends StatelessWidget {
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
var stars = Row(
mainAxisSize: MainAxisSize.min,
children: <Widget>[
Icon(Icons.star, color: Colors.green[500]),
Icon(Icons.star, color: Colors.green[500]),
Icon(Icons.star, color: Colors.green[500]),
Icon(Icons.star, color: Colors.black),
Icon(Icons.star, color: Colors.black),
],
);
final ratings = Container(
padding: const EdgeInsets.all(20),
child: Row(
mainAxisAlignment: MainAxisAlignment.spaceEvenly,
children: <Widget>[
stars,
Text('170 Reviews',
style: TextStyle(
color: Colors.black,
fontWeight: FontWeight.w800,
fontFamily: 'Roboto',
letterSpacing: 0.5,
fontSize: 20,
))
],
),
);
final descTextStyle = TextStyle(
color: Colors.black,
fontWeight: FontWeight.w800,
fontFamily: 'Roboto',
letterSpacing: 0.5,
fontSize: 18,
height: 2,
);
//DefaultTextStyle.merge() allows you to create a default text
//style that is inherited by its child and all subsequent children.
final iconList = DefaultTextStyle.merge(
style: descTextStyle,
child: Container(
padding: const EdgeInsets.all(20),
child: Row(
mainAxisAlignment: MainAxisAlignment.spaceEvenly,
children: <Widget>[
Column(
children: <Widget>[
Icon(
Icons.kitchen,
color: Colors.green[500],
),
Text('PREP:'),
Text('25 min'),
],
),
Column(
children: <Widget>[
Icon(
Icons.timer,
color: Colors.green[500],
),
Text('COOK:'),
Text('1 hr'),
],
),
Column(
children: <Widget>[
Icon(
Icons.restaurant,
color: Colors.green[500],
),
Text('FEEDS:'),
Text('4-6'),
],
)
],
),
));
final titleText = Container(
padding: const EdgeInsets.all(20),
child: Text('Strawberry Pavlova',
style: TextStyle(
fontWeight: FontWeight.w800,
letterSpacing: 0.5,
fontSize: 30,
)),
);
final subTitle = Text(
'Pavlova is a meringue-based dessert named after the Russian ballerina'
'Anna Pavlova. Pavlova features a crisp crust and soft,light inside,'
'topped with fruit and whipped cream.',
textAlign: TextAlign.center,
style: TextStyle(
fontFamily: 'Georgia',
fontSize: 25,
));
final leftColumn = Container(
padding: EdgeInsets.fromLTRB(20, 30, 20, 20),
child: Column(
children: <Widget>[
titleText,
subTitle,
ratings,
iconList,
],
),
);
final mainImage = Image.asset('images/pavlova.jpg', fit: BoxFit.cover);
return Scaffold(
appBar: AppBar(
title: Text('Nesting Rows and Columns'),
),
body: Center(
child: Container(
margin: const EdgeInsets.fromLTRB(0, 40, 0, 30),
height: 600,
child: Card(
child: Row(
crossAxisAlignment: CrossAxisAlignment.start,
children: <Widget>[
Container(
width: 440,
child: leftColumn,
),
mainImage,
],
),
),
),
),
);
}
}Note:Row and Column are basic primitive widgets for horizontal and vertical layouts–these low-level widgets allow for maximun customzation. Flutter also offers specialized,higher level widgets that might be sufficient for you needs. For example,instead of Row you might prefer ListTile,an easy-to-use widget with properties for leading and trailing icons,and up to 3 lines of text. Instead of Column,you might prefer ListView,a column-like layout that automatically scrolls if its content is too long to fit the avaiable space. For more information,see Common layout widgets.
Aligning widgets
You control how a row or column aligns its children using the mainAxisAlignment and crossAxisAlignment properties. For a row,the main axis runs horizontally and the cross axis run vertically. For a column,the main axis runs vertically and the cross axis runs horizontally.
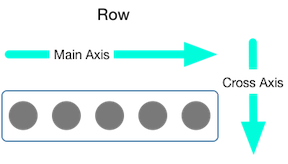
The MainAxisAlignment and CrossAxisAlignment classes offer a variety of constants for controlling alignment.
In the following example,each of the 3 images is 100 pixels wide. The render box(in this case,the entire screen)is more than 300 pixels wide,so setting the main axis alignment to space Evenly divides the free horizontal space evenly between,before,and after each image.
Row(
mainAxisAlignment: MainAxisAlignment.spaceEvenly,
children:[
Image.asset('images/pic1.jpg'),
Image.asset('images/pic2.jpg'),
Image.asset('images/pic3.jpg'),
],
)App source:row_column.

Columns work the same way as rows. The following example shows a column of 3 images,each is 100 pixels high.The height of the render box(in this case,the entire screen) is more than 300 pixels,so setting the main axis alignment to space Evenly divides the free vertical space evenly between,above,and below each image.
Column(
mainAxisAlignment: MainAxisAlignment.spaceEvenly,
children:[
Image.asset('images/pic1.jpg'),
Image.asset('images/pic2.jpg'),
Image.asset('images/pic3.jpg'),
],
)App source: row_column.

Sizing widgets
When a layout is too large to fit a device,a yellow and black striped pattern appears along the affected edge. Here is an example of a row that is too wide:

Widgets can be sized to fit within a row or column by using the Expanded widget. To fix the previoud example where the row of images is too wide for its render box,wrap each image with an Expanded widget.
Row(
crossAxisAlignment: CrossAxisAlignment.center,
children:[
Expaned(
child: Image.asset('images/pic1.jpg'),
),
Expanded(
child: Image.asset('images/pic2.jpg',),
),
Expanded(
child: Image.asset('images/pic3.jpg'),
),
]
)
App source: sizing
Perhaps you want a widget to occupy twice as much space as its siblings. For this,use the Expanded widget flex property,an integer that determines the flex factor for a widget. The default flex factor is 1. The following code sets the flex factor of the middle image to 2.
Row(
crossAxisAlignment: CrossAxisAlignment.center,
children: <Widget>[
Expanded(child: Image.asset('images/pic1.jpg')),
Expanded(
child: Image.asset('images/pic2.jpg'),
flex: 2,
),
Expanded(child: Image.asset('images/pic3.jpg')),
],
),

App source: sizing
Packing widgets
By default,a row or column occupies as much as space along its main axis as possible,but if you want to pack the children closely together,set its mainAxisSize to MainAxisSize.min.The following example uses this property to pack the star icons together.
var stars = Row(
mainAxisSize: MainAxisSize.min,
children: <Widget>[
Icon(Icons.star, color: Colors.green[500]),
Icon(Icons.star, color: Colors.green[500]),
Icon(Icons.star, color: Colors.green[500]),
Icon(Icons.star, color: Colors.black),
Icon(Icons.star, color: Colors.black),
],
);
App source:pavlova
Common layout widgets
Flutter has a rich library of layout widgets. Here are a few of those most commonly used. The intent is to get you up and running as quickly as possible,rather than overwhelm you with a complete list. For information on other available widgets,refer
to the Widget catalog,or use the Search box in the API reference docs. Also,the widget pages in the API docs often make suggestions about similar widgets that might better suit your needs.
The following widgets fall into two categories:standard widgets from the widgets library,and specialized widgets from the Material library. Any app can use the widgets library but only Material apps can use the Material Components library.
Standard widgets
Container :Adds padding,margins,borders,background color,or other decorations to a widget.
GridView :Lays widgets out as a scrollable grid.
ListView:Lays widgets out as a scrollable list.
Stack:Overlaps a widget on top of another.
Material widgets
- Card:Organizes related info into a box with rounded corners and a drop shadow.
- ListTile:Organizes up to 3 lines of text,and optional leading and trailing icons, into a row.
Container
Many layouts make liberal use of Containers to separate widgets using padding,or to add borders or margins. You can change the device’s background by placing the entire layout into a Container and changing its background color or image.
Summary(Container)
Add padding,margins,borders
Change background color or image
Contains a single child widget,but that child can be a Row,Column,or even the root of a widget tree.
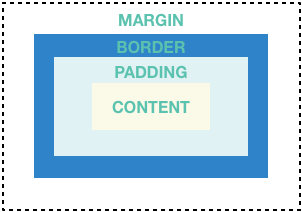
Examples(Container)
This layout consists of a column with two rows,each containing 2 images. A Container is used to change the background color of the column to a lighter grey.
Widget _buildImageColumn() => Container(
decoration: BoxDecoration(
color: Colors.black26,
),
child: Column(
children: <Widget>[
_buildImageRow(1),
_buildImageRow(3),
],
),
);
A Container is also used to add a rounded border and margins to each image:
Widget _buildDecoratedImage(int imageIndex) => Expanded(
child: Container(
decoration: BoxDecoration(
border: Border.all(width: 10, color: Colors.black38),
borderRadius: const BorderRadius.all(const Radius.circular(8)),
),
margin: const EdgeInsets.all(4),
child: Image.asset('images/pic$imageIndex.jpg'),
),
);
Widget _buildImageRow(int imageIndex) => Row(
children: <Widget>[
_buildDecoratedImage(imageIndex),
_buildDecoratedImage(imageIndex + 1),
],
);You can find more Container examples in tutorial and the Flutter Gallery.
App source: container
GridView
Use GridView to lay widgets out as a two-dimensional list. GridView provides two pre-fabricated lists,or you can build your own custom grid. When a GridView detects that its contents are too long to fit the render box,it automatically scrolls.
Summary(GridView)
Lays widgets out in a grid
Detects when the column content exceeds the render box and automatically privdes scrolling
Build your own custom grid,or use one of the provided grids:GridView.count allows you to specify the number of columns
GridView.extent allows you to specify the maximum pixel width of a tile
Note: When displaying a two-dimensional list where it’s important which row and column a cell occupies(for example,it’s the entry in the “calorie”) column for the “avocado” row),use Table or DataTable.
Examples(GridView)

Uses GridView.extent to create a grid with tiles a maximum 150 pixels wide.
App source: grid_and_list
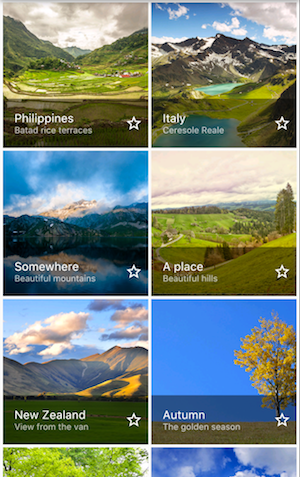
Uses GridView.count to create a grid that’s 2 tiles wide in portrait mode,and 3 tiles wide in landscape mode.The titles are created by setting the footer property for each GridTile.
Dart code: grid_list_demo.dart from the Flutter Gallery
List<Container> _buildGridTileList(int count) => List.generate(
count,
(i) => Container(
child: Image.asset('images/pic${i + 1}.jpg'),
));
Widget _buildGrid() => GridView.extent(
maxCrossAxisExtent: 150,
padding: EdgeInsets.all(4),
mainAxisSpacing: 4,
crossAxisSpacing: 4,
children: _buildGridTileList(4),
);ListView
ListView,a column-like widget,automatically provides scrolling when its content is too long for its render box.
Summary(ListView)
A specialized Column for organizing a list of boxes
Can be laid out horizontally or vertically
Detects when its content won’t fit and provides scrolling
Less configurable than Column,but easier to use and supports scrolling
Examples(ListView)
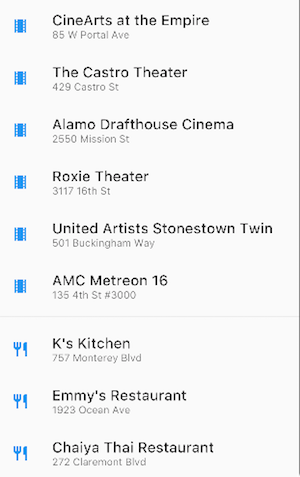
Uses ListView to display a list of business using ListTiles. A Divider separates the theatres from the restaurants.
App source: grid_and_list
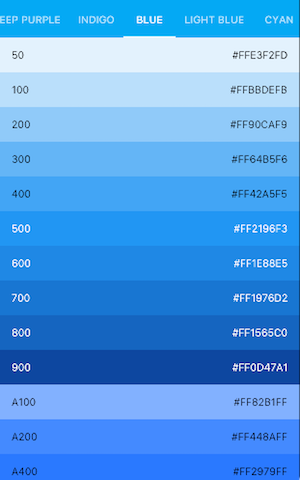
Uses ListView to display Colors from the Material Design palette for a particular color family.
import 'package:flutter/material.dart';
class ListViewDemoPage extends StatelessWidget {
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
ListTile _tile(String title, String subtitle, IconData icon) => ListTile(
title: Text(title,
style: TextStyle(
fontWeight: FontWeight.w500,
fontSize: 20,
)),
subtitle: Text(subtitle),
leading: Icon(
icon,
color: Colors.blue[500],
),
);
Widget _buildList() => ListView(
children: <Widget>[
_tile('CineArts at the Empire', '85 W Portal Ave', Icons.theaters),
_tile('The Castro Theater', '429 Castro St', Icons.theaters),
_tile('Alamo Drafthouse Cinema', '2550 Mission St', Icons.theaters),
_tile('Roxie Theater', '3117 16th St', Icons.theaters),
_tile('United Artists Stonestown Twin', '501 Buckingham Way',
Icons.theaters),
_tile('AMC Metreon 16', '135 4th St #3000', Icons.theaters),
Divider(),
_tile('Kescaped_code#39;s Kithen', '757 Monterey Blvd',
Icons.restaurant),
_tile('Emmyescaped_code#39;s Restaurant', '1923 Ocean Ave',
Icons.restaurant),
_tile('Chaiya Thai Restaurant', '272 Claremont Blvd',
Icons.restaurant),
_tile('La Ciccia', '291 30th St', Icons.restaurant),
],
);
return Scaffold(
appBar: AppBar(
title: Text('ListView Demo'),
),
body: _buildList(),
);
}
}Stack
Use Stack to arrange widgets on top of a base widget–often an image. The widgets can completely or partially overlap the base widget.
Summary(Stack)
Use for widgets that overlap another widget
The first widget in the list of children is the base widget;subsequent children are overlaid on top of that base widget
A Stack’s content can’t scroll
You can choose to clip children that exceed the render box
Examples(Stack)

Uses Stack to overlay a Container(that displays its Text on a translucent black background)on top of a CircleAvatar. The Stack offsets the text using the alignment property and Alignments.
App source: card_and_stack

Uses Stack to overlay a gradient to the top of the image. The gradient ensures that the toolbar’s icons are distinct against the image.
import 'package:flutter/material.dart';
class StackDemoPage extends StatelessWidget {
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
Widget _buildStack() => Stack(
alignment: const Alignment(0.6, 0.6),
children: <Widget>[
CircleAvatar(
backgroundImage: AssetImage('images/pic.jpg'),
radius: 100,
),
Container(
decoration: BoxDecoration(color: Colors.black45),
child: Text('Mia B',
style: TextStyle(
fontSize: 20.0,
fontWeight: FontWeight.bold,
color: Colors.white,
)),
)
],
);
return Scaffold(
appBar: AppBar(
title: Text('Stack Demo'),
),
body: _buildStack(),
);
}
}Card
A Card from the Material library,contains related nuggets of information and can be composed from almost any widget,but is often used with ListTile. Card has a single child,but its child can be a column,row,list,grid,or other widget that supports multiple children,By default,a Card shrinks its size to 0 by 0 pixels. You can use SizedBox to constrain the size of a card.
In Flutter,a Card features slightly rounded corners and a drop shadow,giving it a 3D effect. Changing a Card’s elevation property allows you to control the drop shadow effect. Setting the elevation to 24,for example,visually lifts the Card further from the surface and causes the shadow to become more dispersed. For a list of supported elevation values,see Elevation in the Material guidelines. Specifying an unsupported value disables the drop shadow entirely.
Summary(Card)
Implements a Materical Card
Used for presenting related nuggests of information
Accepts a single child,but that child can be a Row,Column,or other widget that holds a list of children
Displayed with rounded corners and a drop shadow
A Card’s content can’t scroll
Form the Material library
Examples(Card)

A Card containing 3 ListTile and sized by wrapping it with a SizedBox. A Divider separates the first and second ListTiles
App source: card_and_stack
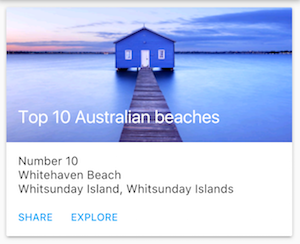
A Card containing an image and text.
Dart code: cards_demo.dart from the Flutter Gallery
import 'package:flutter/material.dart';
class CardDemoPage extends StatelessWidget {
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
Widget _buildCard() => SizedBox(
height: 250,
child: Card(
child: Column(
children: <Widget>[
ListTile(
title: Text(
'1625 Main Street',
style: TextStyle(
fontWeight: FontWeight.w500,
),
),
subtitle: Text('My City,CA 99984'),
leading: Icon(
Icons.restaurant_menu,
color: Colors.blue[500],
),
),
Divider(),
ListTile(
title: Text('(408) 555-1212',
style: TextStyle(
fontWeight: FontWeight.w500,
)),
leading: Icon(Icons.contact_phone, color: Colors.blue[500]),
),
ListTile(
title: Text('costa@example.com'),
leading: Icon(Icons.contact_mail, color: Colors.blue[500]),
)
],
),
),
);
return Scaffold(
appBar: AppBar(
title: Text('Card demo'),
),
body: _buildCard(),
);
}
}ListTile
Use ListTile,a specialized row widget form the Material library,for an easy way to create a row containing up to 3 lines of text and optional leading and trailing icons.
ListTile is most commonly used in Card or ListView,but can be used elsewhere.
Summary(ListTile)
A specialized row that contains up to 3 lines of text and optional icons
Less configurable than Row,but easier to use
Form the Material library
Examples(ListTile)

A Card containing 3 ListTile.
App source: card_and_stack

Uses ListTile to list 3 drop down button types.
Dart code: button_demo.dart from the Flutter Gallery.



